|
High performance plasma amyloid-β biomarkers for Alzheimer's disease
Akinori Nakamura, Naoki Kaneko, Victor L. Villemagne, Takashi Kato, James Doecke, Vincent Dore, Chris Fowler, Qiao-Xin Li, Ralph Martins, Christopher Rowe, Taisuke Tomita, Katsumi Matsuzaki, Kenji Ishii, Kazunari Ishii, Yutaka Arahata, Shinichi Iwamoto, Kengo Ito, Koichi Tanaka, Colin L. Masters & Katsuhiko Yanagisawa
Nature, Published online: 31 January 2018
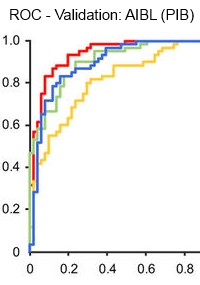
In order to move toward a readily available test for early stages of Alzheimer's disease, the authors have identified and validated blood-based biomarkers for amyloid-β proteins. Using immunoprecipitation with MALDI-TOF MS, they were able to establish that the biomarkers in the IP-MS assay were potentially clinically useful candidates as surrogates for brain amyloid-β burden.
Their retrospective cross-sectional study tested these markers in a discovery data set from the Japanese National Center for Geriatrics and Gerontology (121 samples), and was externally validated using an independent data set derived from the Australian Imaging, Biomarker and Lifestyle Study of Ageing (252 samples).
They also looked at the relationships between the plasma biomarkers and two accepted approaches for amyloid-β determination, positron emission tomography and cerebral spinal fluid biomarkers. These results demonstrate that the three different types of Aβ related biomarkers (plasma and CSF Aβ, and PET imaging), are highly correlated with each other, indicating that plasma Aβ biomarkers are strongly linked with the Aβ status of the CNS.
|
 |